options if your hdd is larger than 1 tb как исправить
Fix External Hard Drive Not Showing Full Capacity on Windows & Mac
If your external hard drive shows the wrong capacity, you will see less space than actual. There are many reasons why your drive is not showing full capacity. Figure out the real causes by reading through this article, and find solutions to restore its full size on both Windows and Mac. The troubleshooting operation might cause data loss, so you need to download EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard to recover important data.
«Why is my Seagate external HDD not showing the true capacity? I use a 4TB external hard drive to create a recovery drive and regular backups. Now with a new laptop, I decided to reformat the drive but Windows says it has only 32GB on it. What’s going on with the rest free space?»
Have you ever encountered a situation when your external hard drive is not showing the full capacity on your Windows PC or Mac? As investigated, this is a common problem for most hard drives made by Seagate, Lacie, Western Digital, or Sandisk larger than 2TB. Yes, it is common to see your 2TB hard drive showing only 500GB, 200GB, 127GB, or 32GB when connected to a computer. But, a hard drive that is under 2TB may also have the same problem. What’s the reason? Can you reclaim the full capacity?
Why does external hard drive not show full capacity?
In most cases, it’s because your hard drive has been initialized to a wrong partition table. As we know, MBR (Master Boot Record) partition table cannot support disk volume space that exceeds 2TB. That’s why owners of 3TB and 4TB hard drives are likely to see less hard drive space than there should be. To solve this type of problem, you need to convert MBR to GPT (GUID Partition Table).
But hard drives less than 2TB are not affected by the MBR limitation, so why do they still have the incorrect size information? In this situation, you should check the hard drive for errors.
Any driver and firmware issues would result in Windows improperly recognizing the drive. Also, computer viruses and hidden recovery partition also tend to cause similar issues.
How to fix wrong capacity issues in Windows [3 fixes]
Typically, when a storage device is not showing the right capacity or space on a Windows PC, the most likely cause of this issue is that the external hard drive driver or firmware is out of date. So, to regain the full capacity displaying on your computer, Method 1 and Method 2 for updating the drive driver and firmware is highly recommended.
Fix 1. Convert MBR to GPT
We introduce two free-to-use methods for you: Windows Disk Management and EaseUS free partition manager. This video tutorial teaches you how to convert MBR to GPT with both tools.
NOTE: You must delete the partition first and then initialize it to GPT in Windows Disk Management. EaseUS Partition Master is able to convert MBR to GPT without data loss, but this technique requires that you download and install the tool in Windows 10/8.1/8/7.
Fix 2. Update external hard drive driver
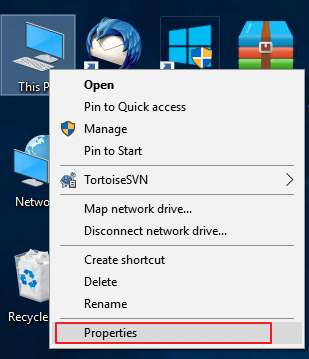
Step 1. Keep your external hard drive connected to your PC, right-click on This PC/My Computer and choose Properties.
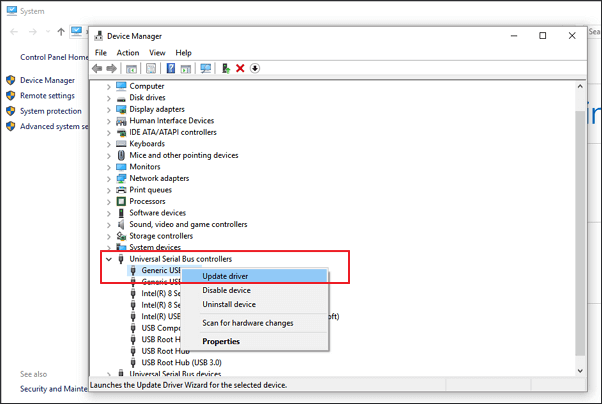
Step 2. Click «device manager» in the left pane and expand «Universal USB Serial Bus controllers».
Then you’ll see a yellow exclamation mark next to the malfunctioning controller. Right-click on it and select «Update driver» or «Update driver software«.
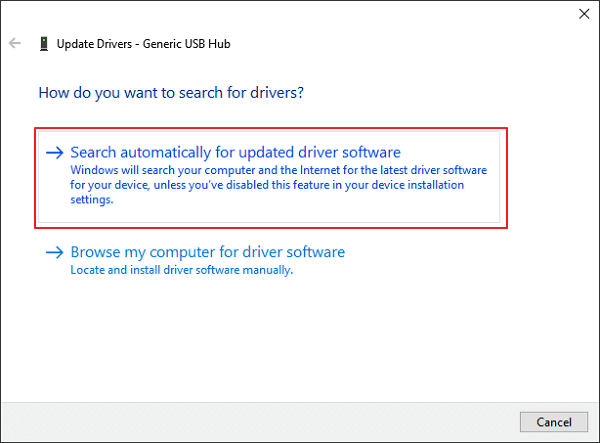
Step 3. Click «Search automaticallyВ for updated driver software».
Fix 3. Update firmware of external hard drive
Step 1. Check the firmware version of your external hard drive
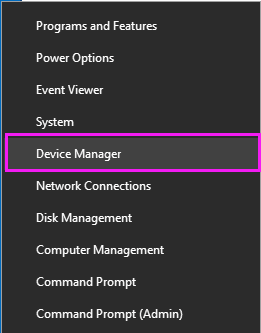
1. Connect your external hard drive to your PC, right-click on the Windows icon, and select Device Manager.
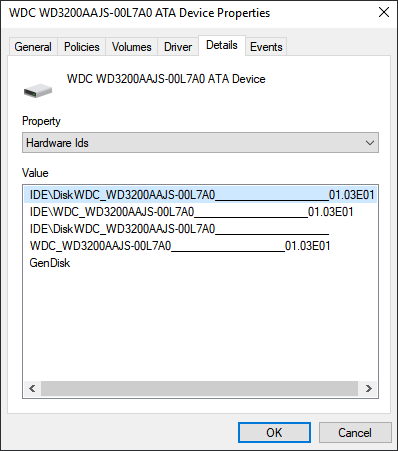
2. Select Disk Drivers, expand it, then find and right-click on your external hard drive, and select Properties.
3. Click «Details» and then select Hardware IDs from the Properties drop-down menu.
The manufacturer and firmware version information will appear in the Value box.
Step 2. Download the firmware update of your external hard drive
1. Go to the website of your external hard drive’s manufacturer and open the support page of the company or search for driver downloads on the website.
2. Click on Support, Download or Drivers.
3. Then enter the model number of your external hard drive or hard drive in Search Knowledgebase, and search Downloads or Model / Parts ID to find the right one.
4. Check for firmware updates.В
If new firmware of your drive is available, click Download, Install or Download Firmware to download and install it to a portable USB drive.
Step 3. Burn downloaded ISO and upgrade the firmware
1. Open the portable USB to which you want to save the firmware ISO of the external hard drive and right-click on the ISO file, then select Burn Disk Image.
2. Insert a writable disk or USB to your PC, select the optical drive from the Drive Burner, and click Burn.
3. Restart your PC with the burned disk or USB drive, press F2, F10, F12, or Esc to bring up BIOS.
4. Select your optical or USB drive using the arrow keys and hit Enter.
5. Follow the firmware upgrade instructions, and when you complete the upgrade process you’ll get a working external hard drive with full capacity. To mitigate the damage from hardware bugs further on, you may also consider using reliable cloud storage on secure hosting for data backups.
How to recover data after restoring hard drive to its full size (Windows & Mac)
If you lose your data while fixing the concerned problem, and you don’t have a backup at hand, download and install EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard to recover lost, deleted, or formatted data on the hard drive. The software has both Windows and Mac OS X/macOS versions. Download the correct version depending on your device.
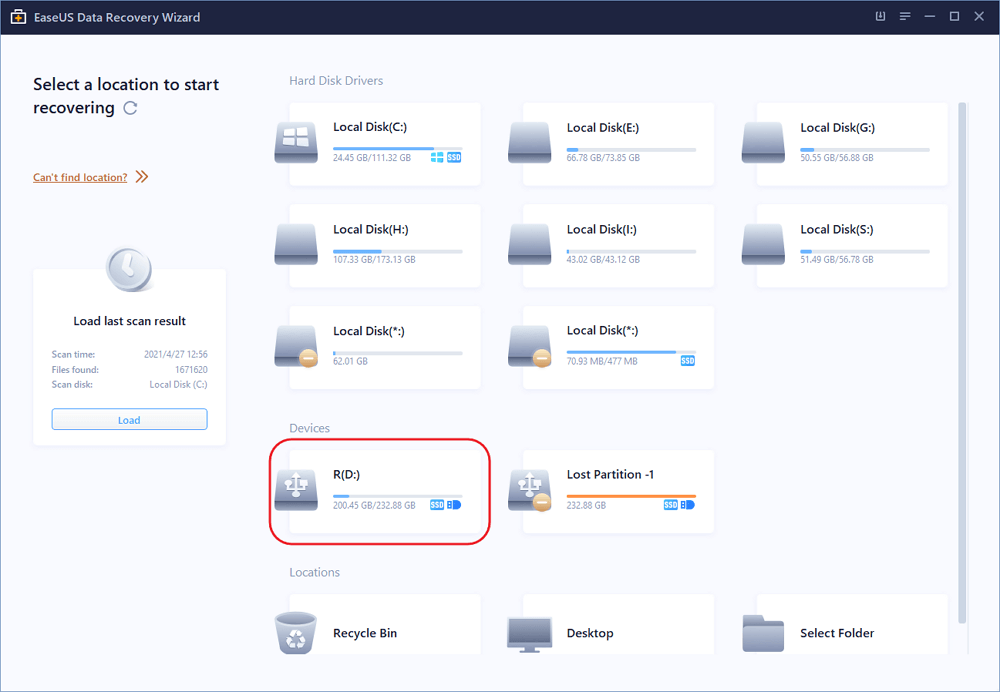
Step 1. Connect the external drive to PC for a scan
Connect the external hard disk to your PC and let Windows recognize the disk and assign it a drive letter. Now launch EaseUS Data Recovery Wizard for Windows. Find your drive you want to recover and click Scan.
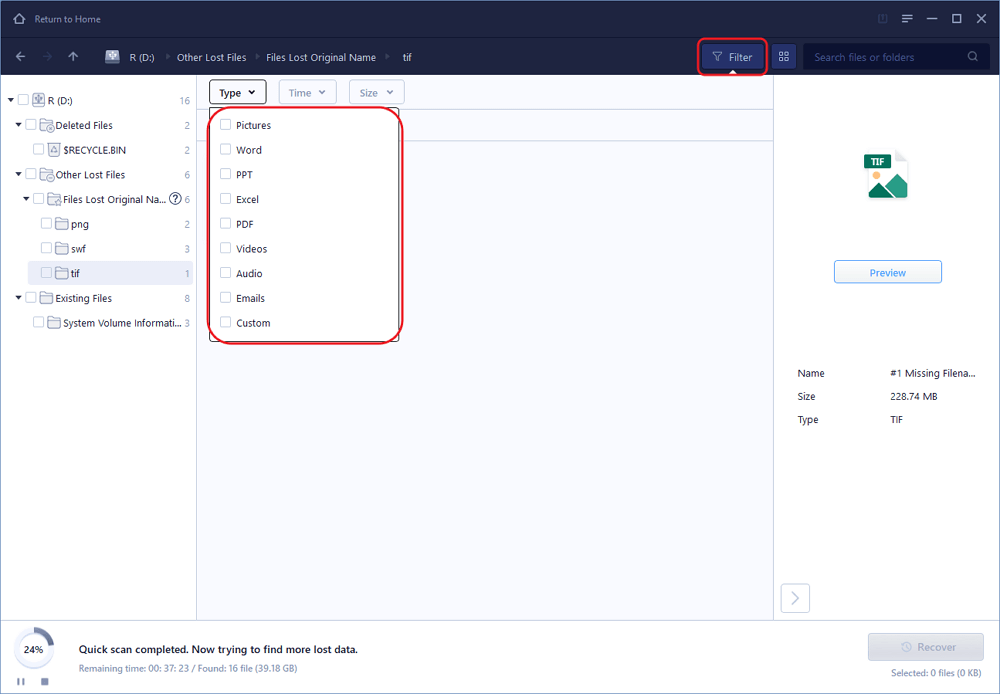
Step 2. Check the scan results
The scan process takes place in two stages, including a quick scan and deep scan. Deep scan is for searching lost data files that even lost file names, so it’s worth waiting longer for the whole scan process to finish and find all desired data. You can try to preview the found files one by one by following their original paths from the leftside tree-view pane, or simply use the Filter function to specify the file type of one kind, like pictures, videos, documents, emails, etc.
Step 3. Select files and recover
Finally, when you are satisfied with the preview results, you can start to select the target files and use the Recover button to get them all back. We suggest you save the recovered files to a location other than the original external hard drive where you lost data.
Drive 0x80 (LBA) : C/H/S=1024/255/63, Count/Size=1953521664/512 Options If Your HDD is Larger Than 1TB.
W indows 7 Setup Complate After Reboot then This Massege Showing «Drive 0x80 (LBA) : C/H/S=1024/255/63, Count/Size=1953521664/512 Options If Your HDD is Larger Than 1TB; Move Your boot file to a saller partition at the start of the HDD. Format the HDD Allow Windows 7 to create a 100 MB boot Partiton. Shrink and Move Your partition with Gparted.
Report abuse
Thank you for posting your question on Microsoft community.
We need some more information about the issue so that we can help you better.
1. What is the make and model of your computer?
2. Have you made any hardware changes to your computer like hard drive replacement?
I appreciate you for providing details about the issue.
This issue may occur due to corrupt or missing Windows startup files.
I would suggest you to run startup repair and check if it helps.
Refer this article:
What are the system recovery options in Windows?
http://windows.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/what-are-system-recovery-options#what-are-system-recovery-options=windows-7
It fixes certain problems, such as missing or damaged system files, that might prevent Windows from starting correctly.
I hope this information helps.
Please do let us know if you need any further assistance.
Исправляем ошибки S.M.A.R.T. на SSD и жестких дисках
Что такое S.M.A.R.T.? Почему возникают SMART ошибки и о чем это говорит? Ниже мы детально расскажем про причины и методы устранения подобных проблем.
Содержание:
Средство S.M.A.R.T., показывающее ошибки жесткого диска (HDD или SSD) является сигналом того, что с накопителем случились какие-то неполадки, влияющие на стабильность и работу компьютера.
Помимо этого, такая ошибка – серьезный повод задуматься о сохранности своих важных данных, поскольку из-за проблемного накопителя можно попросту лишиться всей информации, которую практически невозможно восстановить.
Что такое SMART и что он показывает?
«S.M.A.R.T.» расшифровывается как «self-monitoring, analysis and reporting technology», что в переводе означает «технология самодиагностики, анализа и отчетности».
Каждый жесткий диск, подключённый через интерфейс SATA или ATA, имеет встроенную систему S.M.A.R.T., которая позволяет выполнять следующие функции:
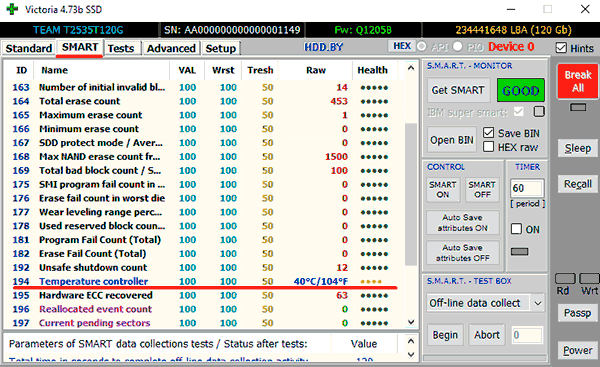
Система S.M.A.R.T. позволяет давать пользователю полную информацию о физическом состоянии жесткого диска методом выставления оценок, при помощи которых можно рассчитать примерное время выхода HDD из строя. С данной системой можно лично ознакомиться, воспользовавшись программой Victoria или другими аналогами.
С тем, как работать, проверять и исправлять ошибки жесткого диска в программе Victoria, Вы можете ознакомиться в статье «Как протестировать и исправить жесткий диск используя бесплатную программу Victoria».
Ошибки S.M.A.R.T.
Как правило, в нормально работающем накопителе система S.M.A.R.T. не выдает никаких ошибок даже при невысоких оценках. Это обусловлено тем, что появление ошибок является сигналом возможной скорой поломки диска.
Ошибки S.M.A.R.T. всегда свидетельствуют о какой-либо неисправности или о том, что некоторые элементы диска практически исчерпали свой ресурс. Если пользователю стали демонстрироваться подобные сообщения, следует задуматься о сохранности своих данных, поскольку теперь они могут исчезнуть в любой момент!
Примеры ошибок SMART
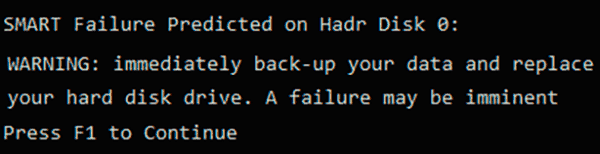
Ошибка «SMART failure predicted»
В данном случае S.M.A.R.T. оповещает пользователя о скором выходе диска из строя. Важно: если Вы увидели такое сообщение на своем компьютере, срочно скопируйте всю важную информацию и файлы на другой носитель, поскольку данный жесткий диск может прийти в негодность в любой момент!
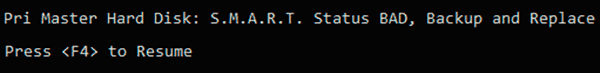
Ошибка «S.M.A.R.T. status BAD»
Данная ошибка говорит о том, что некоторые параметры жесткого диска находятся в плохом состоянии (практически выработали свой ресурс). Как и в первом случае, следует сразу сделать бекап важных данных.
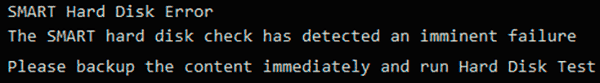
Ошибка «the smart hard disk check has detected»
Как и в двух предыдущих ошибках, система S.M.A.R.T. говорит о скорой поломке HDD.
Коды и названия ошибок могут различаться в разных жестких дисках, материнских платах или версиях BIOS, тем не менее, каждая из них является сигналом для того, чтобы сделать резервную копию своих файлов.
Как исправить SMART ошибку?
Ошибки S.M.A.R.T. свидетельствуют о скорой поломке жесткого диска, поэтому исправление ошибок, как правило, не приносит должного результата, и ошибка остается. Помимо критических ошибок, существуют еще и другие проблемы, которые могут вызывать сообщения такого рода. Одной из таких проблем является повышенная температура носителя.
Ее можно посмотреть в программе Victoria во вкладке SMART под пунктом 190 «Airflow temperature» для HDD. Или под пунктом 194 «Controller temperature» для SDD.
Если данный показатель будет завышен, следует принять меры по охлаждению системного блока:
Другим способом исправления ошибок SMART является проверка накопителя на наличие ошибок.
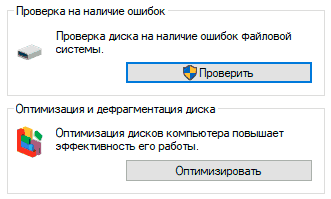
Это можно сделать, зайдя в папку «Мой компьютер», кликнув правой клавишей мыши по диску или его разделу, выбрав пункт «Сервис» и запустив проверку.
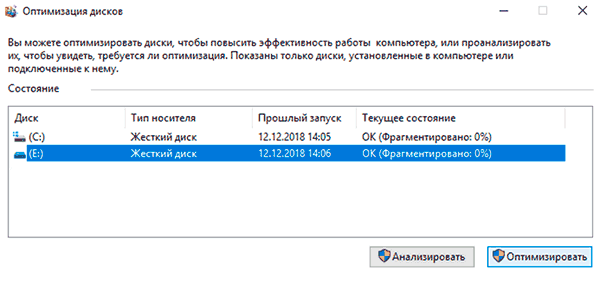
Если ошибка не была исправлена в ходе проверки, следует прибегнуть к дефрагментации диска.
Чтобы это сделать, находясь в свойствах диска, следует нажать на кнопку «Оптимизировать», выбрать необходимый диск и нажать «Оптимизировать».
Если ошибка не пропадет после этого, скорее всего, диск просто исчерпал свой ресурс, и в скором времени он станет нечитаемым, а пользователю останется только приобрести новый HDD или SSD.
Как отключить проверку SMART?
Диск с ошибкой S.M.A.R.T. может выйти из строя в любой момент, но это не означает, что им нельзя продолжать пользоваться.
Стоит понимать, что использование такого диска не должно подразумевать в себе хранение на нем сколько-либо стоящей информации. Зная это, можно провести сброс smart настроек, которые помогут замаскировать надоедливые ошибки.
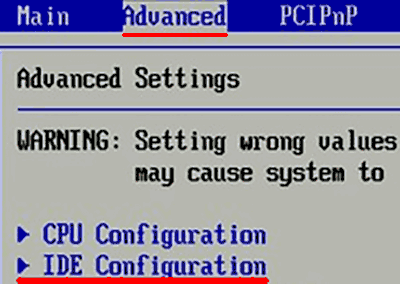
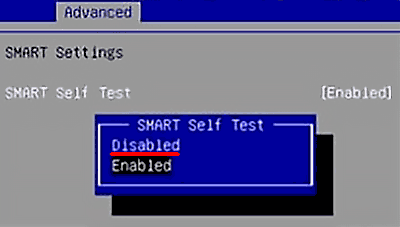
Шаг 1. Заходим в BIOS или UEFI (кнопка F2 или Delete во время загрузки), переходим в пункт «Advanced», выбираем строку «IDE Configuration» и нажимаем Enter. Для навигации следует использовать стрелочки на клавиатуре.
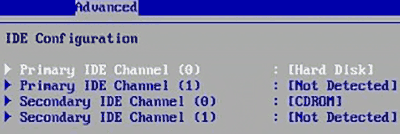
Шаг 2. На открывшемся экране следует найти свой диск и нажать Enter (жесткие диски подписаны «Hard Disc»).
Шаг 3. Опускаемся вниз списка и выбираем параметр SMART, нажимаем Enter и выбираем пункт «Disabled».
Шаг 4. Выходим из BIOS, применяя и сохраняя настройки.
Стоит отметить, на некоторых системах данная процедура может выполняться немного по-другому, но сам принцип отключения остается прежним.
После отключения SMART ошибки перестанут появляться, и система будет загружаться в штатном порядке до тех пор, пока HDD окончательно не выйдет из строя. В некоторых ситуациях ошибки могут показываться в самой ОС, тогда достаточно несколько раз отклонить их, после чего появится кнопка «Больше не показывать».
Что делать если данные были утеряны?
При случайном форматировании, удалении вирусами или утере любых важных данных следует быстро вернуть утерянную информацию самым эффективным методом.
Шаг 1. Установить и запустить программу RS Partition Recovery.
Универсальное решение для восстановления данных
Шаг 2. Выберите носитель или раздел диска, с которого необходимо восстановить данные.
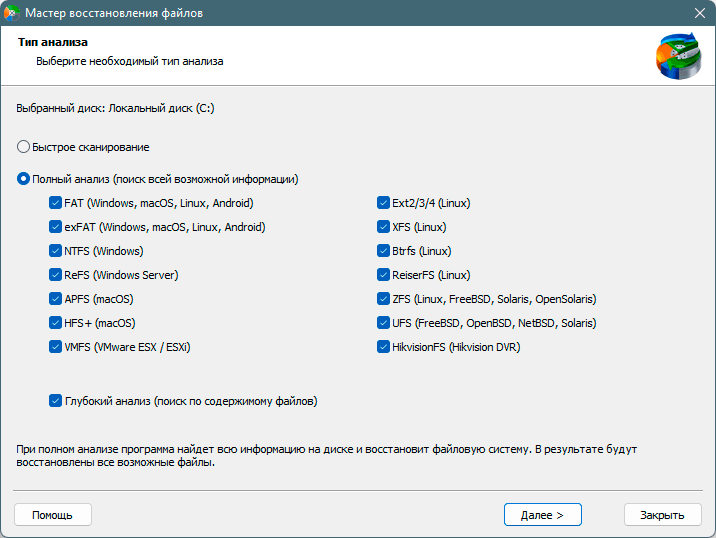
Шаг 3. Выберите тип анализа.
Быстрый анализ стоит использовать, если файлы были удалены недавно. Программа проведет анализ и отобразит данные доступные для восстановления.
Полный анализ позволяет найти утерянные данные после форматирования, перераспределения диска или повреждения файловой структуры(RAW).
Шаг 4. Просмотр и выбор файлов для восстановления.
Шаг 5. Добавление файлов для сохранения в «Список Восстановления» или выбор всего раздела для восстановления.
Стоит отметить, что в качестве места для записи восстановленного файла лучше всего выбрать другой диск или раздел чтобы избежать перезаписи файла.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Это сильно зависит от емкости вашего жесткого диска и производительности вашего компьютера. В основном, большинство операций восстановления жесткого диска можно выполнить примерно за 3-12 часов для жесткого диска объемом 1 ТБ в обычных условиях.
Если файл не открывается, это означает, что файл был поврежден или испорчен до восстановления.
Используйте функцию «Предварительного просмотра» для оценки качества восстанавливаемого файла.
Когда вы пытаетесь получить доступ к диску, то получаете сообщение диск «X: \ не доступен». или «Вам нужно отформатировать раздел на диске X:», структура каталога вашего диска может быть повреждена. В большинстве случаев данные, вероятно, все еще остаются доступными. Просто запустите программу для восстановления данных и отсканируйте нужный раздел, чтобы вернуть их.
Пожалуйста, используйте бесплатные версии программ, с которыми вы можете проанализировать носитель и просмотреть файлы, доступные для восстановления.
Сохранить их можно после регистрации программы – повторное сканирование для этого не потребуется.
Windows support for hard disks that are larger than 2 TB
This article discusses the manner in which Windows supports hard disks that have a storage capacity of more than 2 TB and explains how to initialize and partition disks to maximize space usage.
Applies to: В Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2
Original KB number: В 2581408
Summary
In order for an operating system to fully support storage devices that have capacities that exceed 2 terabytes (2 TB, or 2 trillion bytes), the device must be initialized by using the GUID Partition Table (GPT) partitioning scheme. This scheme supports addressing of the full range of storage capacity. If the user intends to start the computer from one of these large disks, the system’s base firmware interface must use the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) and not BIOS.
This article outlines Microsoft support across all Windows versions since Windows XP. It also describes the requirements to address the full storage capability of these devices.
More information
The management of modern storage devices is addressed by using a scheme called Logical Block Addressing (LBA). It’s the arrangement of the logical sectors that constitute the media. LBA0 represents the first logical sector of the device, and the last LBA designation represents the last logical sector of the device, one label per sector. To determine the capacity of the storage device, you multiply the number of logical sectors within the device by the size of each logical sector. The current size standard is 512 bytes. For example, to achieve a device that has a capacity of 2 TB, you must have 3,906,250,000 512-byte sectors. However, a computer system requires 32 bits (1 s and 0 s) of information to represent this large number. Therefore, any storage capacity that is greater than what can be represented by using 32 bits would require an additional bit. That is, 33 bits.
The problem in this computation is that the partitioning scheme that is used by most modern Windows-based computers is MBR (master boot record). This scheme sets a limit of 32 for the number of bits that are available to represent the number of logical sectors.
The 2-TB barrier is the result of this 32-bit limitation. Because the maximum number that can be represented by using 32 bits is 4,294,967,295, it translates to 2.199 TB of capacity by using 512-byte sectors (approximately 2.2 TB). Therefore, a capacity beyond 2.2 TB isn’t addressable by using the MBR partitioning scheme.
To make more bits available for addressing, the storage device must be initialized by using GPT. This partitioning scheme lets up to 64 bits of information be used within logical sectors. It translates to a theoretical limitation of 9.4 ZB (9.4 zettabytes, or 9.4 billion terabytes). However, the issue that affects GPT is that most currently available systems are based on the aging BIOS platform. BIOS supports only MBR-initialized disks to start the computer. To restart from a device that is initialized by using GPT, your system must be UEFI-capable. By default, many current systems can support UEFI. Microsoft expects that most future systems will have this support. Customers should consult with their system vendor to determine the ability of their systems to support UEFI and disks that have storage capacities that are greater than 2 TB.
Overall requirements for a non-bootable data volume
For a system to be able to address the maximum capacity of a device that has a storage capacity of more than 2 TB, the following prerequisites apply:
The disk must be initialized by using GPT.
The Windows version must be one of the following (32-bit or 64-bit, unless otherwise noted, but including all SKU editions):
The latest storage drivers from your storage controller manufacturer must be installed. For example, if your system uses an Intel storage controller that is set to «RAID» mode, make sure that you have the latest applicable drivers from the Intel support site.
Overall, you should contact your system vendor to determine whether the system supports device sizes of more than 2 TB.
Overall requirements for a bootable system volume
Assume that you want to meet the following conditions:
To meet these conditions, the following prerequisites apply:
The disk must be initialized by using GPT.
The system firmware must use UEFI.
The Windows version must be one of the following (64-bit only, but including all SKU editions):
The latest storage drivers from your storage controller manufacturer must be installed. For example, if your system uses an Intel storage controller set to RAID mode, make sure that you have the latest applicable drivers from the Intel support site.
Windows does not support starting GPT-initialized volumes by using UEFI systems on 32-bit versions of Windows. Also, legacy BIOS systems do not support starting GPT-partitioned volumes. Consult your system vendor to determine whether the system supports both UEFI and the startup of devices that have storage capacities of greater than 2 TB.
Support matrix
The following tables list Microsoft support for the various concepts that are discussed in this article. This information provides an overall support statement about disks that have a storage capacity of greater than 2 TB.
Table 1: Windows support for partitioning schemes as data volumes
| System | MBR | Hybrid-MBR | GPT |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 7 | Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Windows Vista | Supported | Not Supported | Supported |
| Windows XP | Supported | Not Supported | Not Supported |
Hybrid-MBR is an alternative style of partitioning that isn’t supported by any version of Windows.
Table 2: Windows support for system firmware
| System | BIOS | UEFI |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 7 | Supported | Supported |
| Windows Vista | Supported | Supported |
| Windows XP | Supported | Not Supported |
Table 3: Windows support for combinations of boot firmware and partitioning schemes for the boot volume
| System | BIOS + MBR | UEFI + GPT | BIOS + GPT | UEFI + MBR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 7 | Supported | Supported; requires a 64-bit version of Windows | Boot volume not supported | Boot volume not supported |
| Windows Vista | Supported | Supported; requires a 64-bit version of Windows | Boot volume not supported | Boot volume not supported |
| Windows XP | Supported | Not supported | Boot volume not supported | Boot volume not supported |
Table 4: Windows support for large-capacity disks as non-booting data volumes
Capacity beyond 2 TB cannot be addressed by Windows if the disk is initialized by using the MBR partitioning scheme. For example, for a 3-TB single disk that is initialized by using MBR, Windows can create partitions up to the first 2 TB. However, the remaining capacity cannot be addressed and, therefore, cannot be used.
Initialize a data disk by using GPT
The following steps show how to initialize a fresh disk by using the GPT partitioning scheme to help ensure that Windows can address the maximum available storage capacity. Make sure that you back up any important data before you try these steps.
Click Start, type diskmgmt.msc in the Start search box, right-click diskmgmt.msc, and then click Run as Administrator. If it’s necessary, enter the credentials for a user account that has Administrator privileges.
When a non-initialized disk is detected by Windows, the following window opens to prompt you to initialize the disk.
In the Initialize Disk dialog box, click GPT (GUID Partition Table), and then press OK.
If you select this option, this hard disk will not be recognized by Windows versions earlier than and including Windows XP.
Check the Disk Management window to verify that the disk is initialized. If it is, the status row for that disk at the bottom of the window should indicate that the disk is Online.
After the disk is initialized, you must create a partition, and then format that partition by using a file system. It’s to be able to store data in that partition, and assign a name and a drive letter to that partition. To do it, right-click the unallocated space on the right side of the status row for that disk, and then click New Simple Volume. Follow the steps in the partition wizard to complete this process.
Convert an MBR disk to GPT
If you have previously initialized the disk by using the MBR partitioning scheme, follow these steps to initialize the disk by using the GPT scheme. Make sure that you back up any important data before you try these steps.
Click Start, type diskmgmt.msc in the Start search box, right-click diskmgmt.msc, and then click Run as Administrator. If it’s necessary, enter the credentials for a user account that has Administrator privileges.
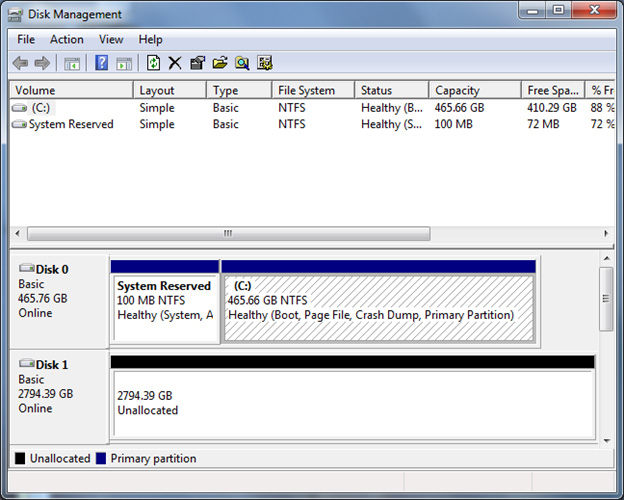
In the Disk Management window, examine the disk status rows at the bottom. In the following example, the user has a 3-TB disk that was previously initialized by using the MBR partitioning scheme. That device is labeled here as Disk 1.
Disk 1 contains two separate unallocated sections. This separation indicates that the first 2 TB of the disk space can be used. However, the remaining space is non-addressable because of the 32-bit addressing space limitation of the MBR partitioning scheme. To enable the system to fully address the total capacity of the storage device, you must convert the disk to use the GPT partitioning scheme.
Right-click the label on the left for the disk that you want to convert, and then click Convert to GPT Disk.
The display should now show that the full amount of available space in unallocated.
Now that the disk is initialized to access the full storage capacity, you must create a partition, and then format that partition by using a file system. It’s to be able to store data in that partition, and assign a name and a drive letter to that partition. To do it, right-click the unallocated space on the right side of the status row for that disk, and then click New Simple Volume. Follow the steps in the partition wizard to complete this process.
Known issues or limitations
Because the transition to a single-disk capacity of greater than 2 TB has occurred fairly recently, Microsoft has investigated how Windows supports these large disks. The results reveal several issues that apply to all versions of Windows earlier than and including Windows 7 with Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2008 R2 with Service Pack 1.
To this point, the following incorrect behavior is known to occur when Windows handles single-disk storage capacity of greater than 2 TB:
The numeric capacity beyond 2 TB overflows. It results in the system being able to address only the capacity beyond 2 TB. For example, on a 3-TB disk, the available capacity may be only 1 TB.
The numeric capacity beyond 2 TB is truncated. It results in no more than 2 TB of addressable space. For example, on a 3-TB disk, the available capacity may be only 2 TB.
The storage device isn’t detected correctly. In this case, it isn’t displayed in either the Device Manager or Disk Management windows. Many storage controller manufacturers offer updated drivers that provide support for storage capacities of more than 2 TB. Contact your storage controller manufacturer or OEM to determine what downloadable support is available for single-disk capacities that are greater than 2 TB.
SCSI sense data
When a disk encounters errors that are related to unreadable or unwritable sectors, it reports those errors and the relevant SCSI sense data to the operating system. SCSI sense data may contain information about LBA for sectors that were found to be unreadable or unwritable.
For LBA address space that is greater than 2 TB, the disk requires SCSI sense data in Descriptor format. This format isn’t supported by Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2, which retrieves SCSI sense data in Fixed format. Therefore, the retrieved SCSI sense data either does not contain information about bad sectors or it contains incorrect information about bad sectors. Administrators should note this limitation when they look for bad sector LBA information that’s recorded in the Windows event log.