out of memory blender как исправить
Многие пользователи ПК во время работы с какой-либо программой могут столкнуться с «вылетом» указанной программы, и появившимся сообщением «Out of memory». Возникшая проблема может иметь множество причин, начиная от банального недостатка памяти на пользовательском ПК, и заканчивая некорректной работой с памятью какой-либо программы.
Причины появления дисфункции
Сообщение «Out of memory» (в переводе дословно «вне памяти», или «недостаточно памяти») обычно возникает при недостатке памяти на пользовательском компьютере. В частности же, в появлении данной ошибки «виновен» следующий набор факторов:
Когда вашему компьютеру не хватает физической R.A.M. памяти, он заимствует часть места на жёстком диске, и создаёт так называемую «виртуальную память». Система временно хранит в такой виртуальной памяти ту часть данных, которая не помещается в памяти обычной. Такие данные обычно хранятся в файле «pagefile.sys», размер которого может увеличиваться или уменьшаться в зависимости от специфики работы вашей ОС. Если на диске будет недостаточно места, файл «pagefile.sys» не сможет расти, и пользователь получит рассматриваемую ошибку.
Как исправить ошибку «Out of memory»
Для решения указанной проблемы рекомендую сделать следующее:
Альтернативным вариантом решения проблемы является установка соответствующего фикса от Майкрософт. Или использование расширений или дополнений для браузера уровня «The Great Suspender» для «Google Chrome», хорошо работающего с ненужными вкладками браузера.
bcdedit/set IncreaseUserVa 3072
И нажмите на ввод, и перезагрузите ваш ПК. Функционал данной команды позволяет выделить пользовательским приложениям 3 гигабайта оперативной памяти для работы. В некоторых системах этого может быть слишком много, потому если после ввода данной команды система начала чаще сбоить, то введите в командной строке от имени администратора:
bcdedit /set IncreaseUserVa 2560 — что позволит задействовать 2,5 гигабайта вместо ранее забронированных 3.
Если ситуацию этим исправить не удалось, верните настройки на состояние по умолчанию:
bcdedit /deletevalue IncreaseUserVa
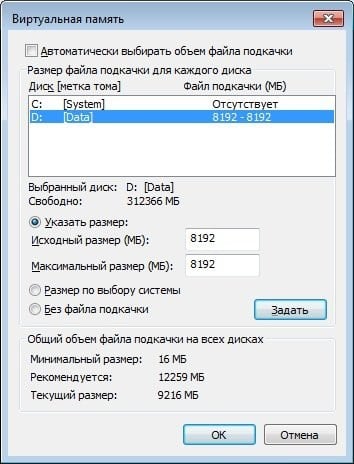
Установите нужный размер файла подкачки
Заключение
Ошибка «Out of memory» может иметь множество причин, связанных как с физическим недостатком памяти на ПК, так и другими детерминантами, изложенными мной выше. Для решения проблемы советую закрыть ненужные программы (вкладки браузера) на вашем компьютере (тем самым разгрузив его память), а самым эффективным инструментом является установка дополнительной планки памяти на ПК, что в большинстве случаев поможет избавиться от ошибки на вашем компьютере.
Memory optimization for rendering in Blender
When it comes to rendering large and intensive scenes in Blender, memory optimization becomes critical. I have lost count of how many times Blender crashed for me thanks to using too much memory during rendering. Many times, the statement less is more, is something to really keep in mind.
These are the primary ways in which we can reduce memory usage in Blender.
There are a lot of parameters that dictate memory usage. In this article we will take a deep dive in RAM usage for Blender users and what we can do to be more efficient with our RAM so that we may render those large projects that otherwise leave us with a crash or out of memory error.
How does RAM work in a computer?
In a computer, the operating system is responsible for managing memory. It allocates memory for applications upon request and free memory when it is no longer needed based on what the user is currently doing and what different processes are running. Both in the foreground and in the background.
For instance, the operating system knows what application is currently being used actively and so it prioritizes memory for it along with other resources such as CPU and disk access depending on what it needs.
In the meantime, other applications that are minimized or has not been active for a long time gets less and less priority. At some point the operating system can even start to move data from RAM to the hard drive for later if applications are open for longer periods in the background but isn’t vital enough to store in the faster RAM.
On Windows this space on the hard drive is called the swap file while on MacOS and Linux, this isn’t a file. Instead, it is a dedicated part of the hard drive called a swap partition.
So, what does this have to do with rendering in Blender?
Why does Blender crash during rendering?
The most common cause for Blender to not be able to complete a render is that it runs out of available RAM. This can be system RAM, or it can be your VRAM that is handled by your graphics card (GPU).
In most cases, if we have a dedicated graphics card, we can use it to render our scenes in Blender. Either with Cuda or Optix if we have an Nvidia card, or with OpenCL with AMD cards. If not, we can render with CPU.
No matter what compute device we choose to use, we still need to fit the data needed for rendering in the available RAM. If not, Blender crashes.
There are other reasons why Blender may crash during rendering, such as a bug in Blender or a graphics driver that isn’t co-operating. If this is the case for you, you can read my article on common render problems to get some guidance on what driver to use for your graphics card.
These days, if we use a GPU to render, Blender can use both the GPUs VRAM and the system RAM when the VRAM becomes full. So, deciding between CPU and GPU based on the available VRAM and the size of a scene has become less of an issue.
However, we are still limited by the total amount of available memory and so Blender may still crash, so what can we do?
What can we do when Blender run out of memory during rendering?
From a birds-eye view there are two things we can do. We can free up more memory and we can reduce the amount of memory used by Blender during rendering.
In many cases, we start in the second category. By reducing memory used in a scene. This is usually where we can gain most because many scenes are overwhelmingly unoptimized.
Here is a list of the primary things that can have a significant impact in reducing memory usage for our scenes.
Some settings and features that has little to no memory impact on the other hand are things like number of light paths and samples. Also, the tile size is something that gets brought up as optimizations.
These are all valuable settings when we want to optimize the use of the CPU and GPU and improve render time. But they have almost no impact on memory usage.
We must distinguish between feature that impact memory vs CPU or GPU computations.
Let’s look at each of the primary ways to reduce memory used by our scene before we move on to how we can free up memory for use in the scene in other areas.
How can we reduce memory used by geometry in Blender?
Our geometry uses a lot of RAM. When we experience problem with rendering thanks to the lack of RAM, reducing geometry is one of the most straight forward ways to improve the situation.
There are several ways we can reduce the amount of geometry in a Blender scene. Here are the ones we will cover.
Reduce memory usage by reducing subdivision and multires modifier levels
Let’s start by looking at the subdivision surface modifier. This modifier quadruples the amount of geometry for every level of subdivisions we add.
Four times as much data uses up for times as much memory and starting to look through objects where you have a subdivision and decreasing it as much as possible can be enough to save a scene that isn’t rendering.
Personally, I try to stick to subdivision levels of 1-3. What you need to keep in mind is that you are far more involved in your project than anybody else. Nobody else see your scene at the same detailed level.
It is rare that people viewing your art complain about an extra level of subdivision if you yourself can barely see the difference. In these cases, the extra geometry is simply not worth the extra memory usage.
The same goes for the multi-resolution modifier. You can stick to 1 level lower than you think you need in most cases.
Reduce memory usage by removing objects and geometry
Any object, vertex, edge or face we can remove is an element we don’t need to load into memory.
In many projects we render a lot more objects than we need. For instance, in landscape scenes, we often keep a lot more landscape around that isn’t in view of the camera.
Some of these objects may be needed because they contribute to reflections or shadows in the cameras view. But everything that isn’t contributing can simply be removed.
We can also intelligently divide the scene into multiple render layers, rendering them separately and combine them again in the compositor. Just keep in mind that elements that has an influence on each other need to be rendered on the same layer.
Another example is if we are rendering a huge object, such as a skyscraper, castle or mountain, we could potentially remove geometry from the backside, only rendering the portion that actually face the camera.
If you are making multiple shots or animations, you can keep a major scene file that you copy and remove anything you don’t need for that particular shot. Then do the same for each shot before finally editing them together in the VSE or an external video editor.
Reduce memory by using adaptive subdivision
Adaptive subdivision is an experimental feature available in Cycles. Even if it is still considered experimental, it has been around for a long time. Personally, I find it to be stable enough to be used in everyday modeling.
Instead of giving an object a fixed subdivbision, Blender subdivide the object depending on the objects distance from the camera.
Geometry further away get less subdivisions while objects closer to the camera get more dense geometry.
The downside is that it can be challenging to tweak the adaptive subdivision to fit the scene perfectly. With its default settings it tends to add very much geometry for very fine detailed meshes.
This may lead to the opposite effect, using more geometry and memory than initially. So, it is important to tweak and test the settings before committing to a full-scale render.
Another downside is that we can only view the result in rendered mode as the subdivision happens at render time. But we can view the result in rendered preview mode.
To setup adaptive subdivision for an object in Blender follow these steps:
It is common to use adaptive subdivision together with shader displacement. You can read more about displacement and how to set it up here:
The primary settings to keep in mind when tweaking the adaptive subdivision are the dicing rate render and max subdivisions.
A lower dicing rate will cause more geometry while the max subdivisions set the max allowed subdivisions overall.
Link instead of duplicating data with Alt+D
Very often we are taught that to duplicate an object, use Shift+D. This command duplicates both the object and the mesh, making a completely new copy in memory.
If we intend to not change the duplicate, but keep it just as the original, we can save a lot of memory by using alt+d to link the data instead.
With alt+d we create a new object, but we let it point to the original mesh data inside the original object. Now we have two objects that look the same with minimal RAM footprint.
How can we reduce memory used by materials and textures in Blender?
Here we have two options. Removing textures that are not needed or use a lower resolution texture if possible. We will start by looking at ways we can remove certain texture types and replace them with something else. Then we will look at a few ways to quickly manage texture sizes.
When working with PBR materials we most often have these texture maps:
The easiest image texture to remove is the roughness. But this map is also the most creative map so, depending on how we use it we may or may not have an easy time removing it to save memory.
For instance, if we are using overlays with the roughness and play of light is a big part of our scene, we may just not want to replace it.
In many cases though we can use one of the red, green, or blue channels of the diffuse texture instead of a separate image texture map for roughness.
This is what it could look like.
In this case we get a pattern that matches the diffuse texture while not losing much of the original roughness texture. This is also a very rough surface to begin with, just like most surfaces we encounter.
In these cases we rarely see a difference between an accurate roughness map and this method.
Sometimes we can also replace the normal map with a bump node with input from the diffuse texture or one of the single channels as well. But in general, we get a much finer and more even detail with this method than a normal map. So the method is much more limited.
This is how to set it up.
For instance, if this surface was covered with grass, this may be enough to give us a realistic enough ground plane.
The second way we can reduce memory used by a material is to use lower resolution textures. Simply bring your image texture into a 2D photo image editor like photoshop, affinity photo or gimp and reduce the size.
Computers store data in increments to the power of two. So, the most efficient textures to store are sizes like 512, 1024, 2048 4096 and so on.
A texture with the size of 2048 by 2048 takes only a quarter of the memory compared to a 4096 by 4096 texture.
We can also reduce the size of all textures in Blender simultaneously by using the simplify options. We cover this later in this article.
How can we reduce memory used by particle systems in Blender?
Another substantial source of memory usage is particle systems that we use to distribute objects.
The most common use of particle systems is to distribute a collection of objects across a surface. But there are other uses as well, and depending on your situation you may have different flexibility with how much RAM you can save by optimizing it.
But for the common cases when we distribute objects across a surface, such as grass, greenery, or rocks on the ground or debris in an old house we can use child particles and limit the area we distribute the particles across.
There are two types of child particles distributions. Simple and interpolated. Essentially, they are two different mathematical ways to distribute particles with different settings.
The simple child distribution uses the parent particles position as a starting point when emitting while the interpolated child particles emit between parents and can also themselves become virtual parents.
You can read more about child particles in the Blender manual here.
Personally, I tend to use the interpolated child particles most of the time as it gives more options and a more even distribution.
Before you turn child particles on, reduce your number of particles to one tenth or one hundredths of the original amount so that you avoid Blender freezing for too long and potentially crashing.
The default setting is to emit 10 particles per parent in the viewport and 100 in the final render creating a much denser distribution. You can change these values in the particle system child settings.
Once child particles are setup, we can also create a vertex group if we have some vertex density across our surface. Go to weight paint and paint the area that is in view of the camera.
Then in the particle system settings, find the vertex groups section and the density parameter and select your vertex group here.
This will limit the distribution of particles to only the painted area so that we don’t have to emit unnecessary particles that don’t contribute to the scene.
Using the simplify settings to reduce memory usage
The simplify settings are excellent when we need a quick fix to a heavy scene. We can use the simplify settings to globally reduce memory usage in a few different ways. The simplify settings can be found in the render settings. To enable them tick the checkbox on the simplify section.
The simplify options are slightly different between Eevee and Cycles. But generally, they are the same. I cover the simplify section for Cycles as part of this article here, but we will cover it in this article as well:
Here are the settings.
We can set a max subdivision for all objects in the entire scene. This is a quick way to reduce geometry to a manageable level if you know you have many objects with too much geometry.
The child particles slider is a percentage value from 0 to 1. Decreasing the slider to 0.5 will remove 50% of the child particles for all particle systems in the scene for example.
Texture limit allow us to set a maximum texture size through the entire scene. Any texture larger than this number will be downsized automatically. This however, is only available in Cycles.
The AO bounces isn’t really applicable to memory optimization but if you want to know more about it you can read the article linked above.
For Cycles we also have culling in the simplify settings. These are two checkboxes. Camera culling and distance culling.
Distance culling will take objects that are further than the distance specified away from the camera and not render them in the scene.
The Camera culling will disable objects outside the camera’s visibility to the left, right as well as above and below. The distance is decided by the slider next to the camera culling option.
For an object to be considered for camera or distance culling though, we need to enable culling for all objects that we want to be affected.
We can do this on an object-by-object basis by selecting an object, go to the object properties and find the visibility section.
Here we find the culling subsection with two checkboxes. One for camera cull and one for distance cull.
To enable these checkboxes for multiple objects, we can select all objects we want to cull, then select one object last to become the active object.
After that, enable culling, right click each checkbox, and choose «Copy to selected». This will copy the specific setting from the active object to all selected objects.
Reduce memory used by Blender by rendering from the command line
If we are still struggling to get our scene down in size, we can try to render from the command line. This way, we don’t need the scene open in the interface while rendering, saving us memory during render time.
To render from the command line, on Windows, browse for your Blender installation folder from the command prompt and write the following command:
This will render the first frame in this blend file with the settings used from the blend file in question.
You can find more command line options in the Blender manual here:
How can we free up memory used by other applications?
The last option we will explore is simply to make sure that the system uses as little ram as possible elsewhere. We can do this by opening the task manager on Windows with Ctrl+Alt+Delete or Ctrl+Shift+ESC.
Sort your open applications by memory usage and see what software is using up the most RAM. Blender is likely one of them. If there are others like your web browser or other open applications, you can close them to free up memory during rendering.
Final thoughts
There are quite a few considerations we can keep in mind as we create our scenes. Not only artistic, but also technical that can help us not only improve the memory usage, but also give us a smoother work experience along the way.
In this article we covered a handful of ways we can use to improve our use of memory and potentially render scenes that we previously was not able to.
Error : out of memory
I have a model and when i press shit+z to render view or final render it gives and error out of memory. I tried on both cpu and gpu but the result is same error and stop there. How can i get rid of it and render my scene. Any suggestion or help to render.
GPU mode
CPU mode
When i open the file memory usage
3 Answers 3
You may have the installed RAM for 8GB but you do not have 64-bit Windows software, you are using 32-bit software which restricts your system to below 4GB of usable RAM, to solve this issue you will need to render this on a 64-bit system so it can enough RAM to render. The reason the error occurs again with your graphics card is because it is only 2GB and also is below what the scene requires for rendering, remember that the RAM from your graphics card is separate from your desktop memory so it is not «extra» ram per se, you have these options:
Strip the scene back to the bare minimum so that your system can handle it
Upgrade your GPU to have higher VRAM which will support the render
Get 64-bit software to make use of the full 8GB of RAM which is installed
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged rendering or ask your own question.
Linked
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
site design / logo © 2021 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under cc by-sa. rev 2021.9.17.40238
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
Как исправить проблему переполнения памяти при запекании системы частиц?
Главная › Форумы › Частицы и физика › Как исправить проблему переполнения памяти при запекании системы частиц?
Уважаемые блендероводцы! 🙂
Может кто сможет помочь, или хотя бы подтолкнуть к решению? Я уже отчаялся 🙂
Пишу диплом связанный с трёхмерным моделированием и системами частиц.
Имеется blender сцена в которой 14 систем частиц (2 из них с ключевой физикой, остальные с ньютоновской).
Имеется таймлайн в 400 кадров со всеми нужными анимациями.
Процесс запекания останавливается на 230 кадре по причине переполнения памяти.
Некоторое время назад была такая ошибка, и действительно, blender занимал 7Гб RAM из 8Гб, нашёл программу Cacheman, которая ограничивает программе выделяемую память, после ограничения памяти, Blender’у удалось запечь анимацию до конца, один раз, после этого проблема вернулась.
Но при этом Blender занимает чуть более 1Гб, остальное место занято, я так понимаю, кэшированными данными (см. скриншот https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B4ByZ11rOwE-aGNPSHVkbnIxbHM/view?usp=sharing).
Файл подкачки включён, под файл подкачки выделено более 50Гб, но он не используются даже наполовину.
Полное запекание длилось около 7 часов, ставлю на ночь, и так уже много ночей и “переполнение памяти” 🙁
Кстати, при запекании с определенного места, допустим с середины, источники частиц заново рождают частицы, поэтому частями запекать не получается.
При последнем удачном запекании, в Blender, в настройках кэша указал “кэш на диске” и убрал флажок “Библиотека”. Но сейчас и это не помогает.
Лично я с подобным никогда не сталкивался (даже на ноутбуке с 4ГБ). Точно знаю два варианта: найти знакомого с 16-32 ГБ и попросить или же уменьшить количество самих частиц в каждой системе (у тебя их видимо очень много раз 7 часов печет). Других вариантов не знаю 🙁
Визуализация на GPU
GPU rendering is only supported on Windows and Linux; macOS is currently not supported.
Supported Hardware
Blender supports different technologies to render on the GPU depending on the particular GPU manufacture.
Nvidia
CUDA requires graphics cards with compute capability 3.0 and higher. To make sure your GPU is supported, see the list of Nvidia graphics cards with the compute capabilities and supported graphics cards.
Open Shading Language
Advanced volume light sampling to reduce noise
OptiX
OptiX requires graphics cards with compute capability 5.0 and higher. To make sure your GPU is supported, see the list of Nvidia graphics cards OptiX works best on RTX graphics cards with hardware ray tracing support (e.g. Turing and above).
Open Shading Language
Advanced volume light sampling to reduce noise
Трассировка путей с расщеплением
On Windows and Linux, the latest Pro drivers should be installed from the AMD website.
Open Shading Language
Advanced volume light sampling to reduce noise
Intel
Open Shading Language
Advanced volume light sampling to reduce noise
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Почему Blender перестаёт отвечать во время визуализации?
While a graphics card is rendering, it cannot redraw the user interface, which makes Blender unresponsive. We attempt to avoid this problem by giving back control over to the GPU as often as possible, but a completely smooth interaction cannot be guaranteed, especially on heavy scenes. This is a limitation of graphics cards for which no true solution exists, though we might be able to improve this somewhat in the future.
Если у вас есть возможность, лучше установить более одного GPU и использовать один из них для отображения, а остальные задействовать для визуализации.
Почему сцена, которая визуализируется на центральном процессоре, не визуализируется на видеокарте?
There may be multiple causes, but the most common one is that there is not enough memory on your graphics card. Typically, the GPU can only use the amount of memory that is on the GPU (see Would multiple GPUs increase available memory? for more information). This is usually much smaller than the amount of system memory the CPU can access. With CUDA and OptiX devices, if the GPU memory is full Blender will automatically try to use system memory. This has a performance impact, but will usually still result in a faster render than using CPU rendering. This feature does not work for OpenCL rendering.
Можно ли для визуализации использовать несколько видеокарт?
Могут ли несколько видеокарт увеличить доступную память?
What renders faster, Nvidia or AMD, CUDA, OptiX or OpenCL?
This varies depending on the hardware used. Different technologies also have different compute times depending on the scene tested. For the most up to date information on the performance of different devices, browse the Blender Open Data resource.
Сообщения об ошибках
In case of problems, be sure to install the official graphics drivers from the Nvidia or AMD website, or through the package manager on Linux.
Unsupported GNU version
On Linux, depending on your GCC version you might get this error. See the Nvidia CUDA Installation Guide for Linux for a list of supported GCC versions. There are two possible solutions to this error:
Use an alternate compiler
If you have an older GCC installed that is compatible with the installed CUDA toolkit version, then you can use it instead of the default compiler. This is done by setting the CYCLES_CUDA_EXTRA_CFLAGS environment variable when starting Blender.
Launch Blender from the command line as follows:
(Substitute the name or path of the compatible GCC compiler).
Remove compatibility checks
If the above is unsuccessful, delete the following line in /usr/local/cuda/include/host_config.h :
This will allow Cycles to successfully compile the CUDA rendering kernel the first time it attempts to use your GPU for rendering. Once the kernel is built successfully, you can launch Blender as you normally would and the CUDA kernel will still be used for rendering.
CUDA Error: Kernel compilation failed (Ошибка CUDA: Сбой компиляции ядра)
This error may happen if you have a new Nvidia graphics card that is not yet supported by the Blender version and CUDA toolkit you have installed. In this case Blender may try to dynamically build a kernel for your graphics card and fail.
В таком случае вы можете:
Check if the latest Blender version (official or experimental builds) supports your graphics card.
Если вы сами собирали Blender, попробуйте скачать и установить новейший набор инструментов для разработчика CUDA.
Обычным пользователям не требуется устанавливать набор инструментов CUDA, поскольку Blender уже поставляется со скомпилированными ядрами.
CUDA Error: Out of memory (Ошибка CUDA: Не хватает памяти)
This usually means there is not enough memory to store the scene for use by the GPU.
One way to reduce memory usage is by using smaller resolution textures. For example, 8k, 4k, 2k, and 1k image textures take up respectively 256MB, 64MB, 16MB and 4MB of memory.
The Nvidia OpenGL driver lost connection with the display driver
If a GPU is used for both display and rendering, Windows has a limit on the time the GPU can do render computations. If you have a particularly heavy scene, Cycles can take up too much GPU time. Reducing Tile Size in the Performance panel may alleviate the issue, but the only real solution is to use separate graphics cards for display and rendering.
Another solution can be to increase the time-out, although this will make the user interface less responsive when rendering heavy scenes. Learn More Here.
CUDA error: Unknown error in cuCtxSynchronize() (Ошибка CUDA: Неизвестная ошибка в cuCtxSynchronize())
An unknown error can have many causes, but one possibility is that it is a time-out. See the above answer for solutions.
© Copyright : This page is licensed under a CC-BY-SA 4.0 Int. License. Обновлено: 09/17/2021.