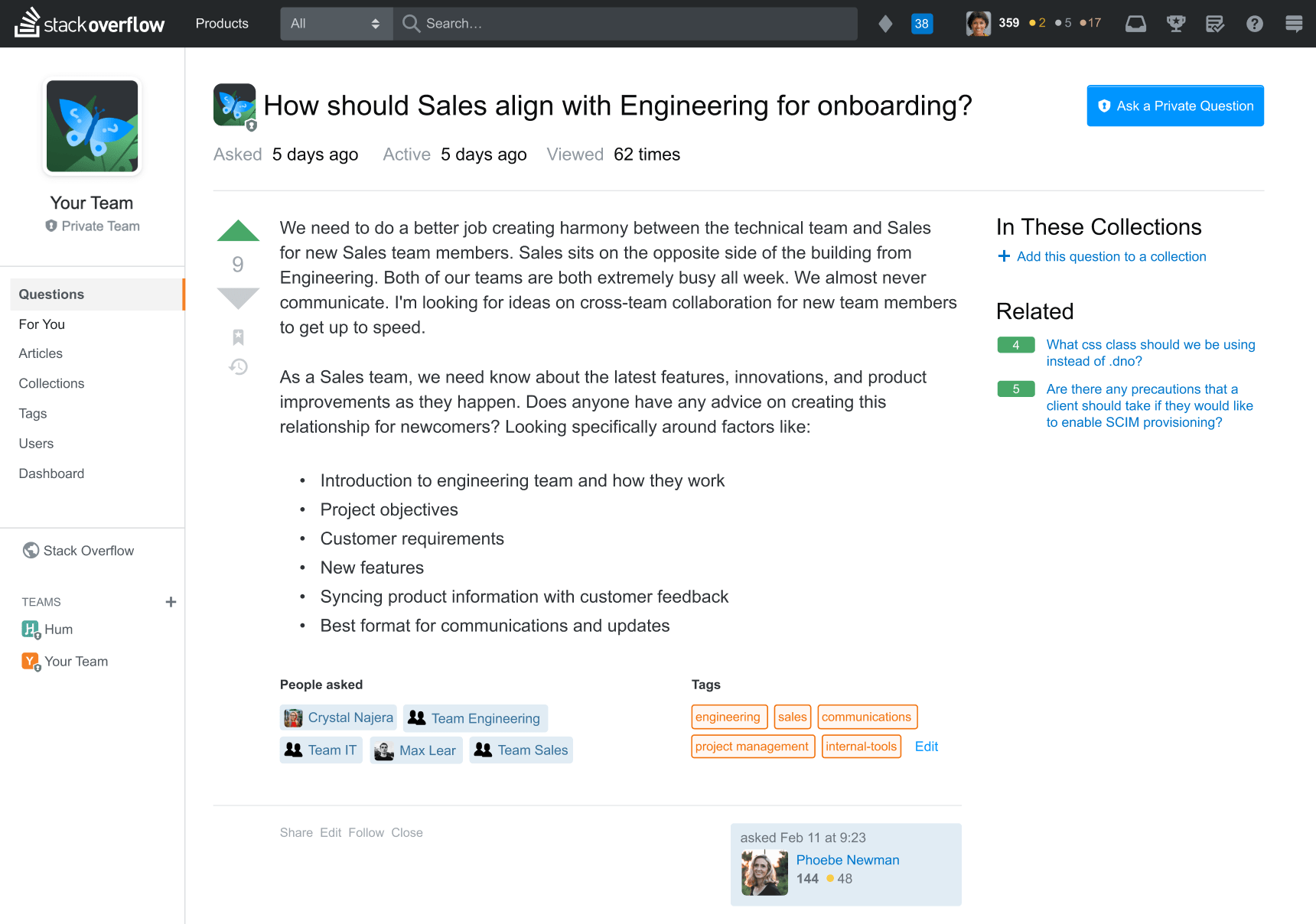
site redirect to another site
Redirects: 301, 302, 307 | How-To 301 guide
What is redirection?
Redirection is a way of forwarding the user to the URL that is different from the one they initially clicked on. Down below some of the most common types of redirection are listed.
301 Moved Permanently
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect which passes between 90-99% of link equity (ranking power) to the redirected page. 301 signals that the page has been moved to another URL and the old URL is outdated.
302 Found (HTTP 1.1) / Moved Temporarily (HTTP 1.0)
302 is a temporary redirect which passes 0% of link equity, and shouldn’t be used in most cases.
As of now, the internet runs on an HTTP protocol which dictates how URLs work. In two versions of this protocol, the HTTP response status code is different:
307 Moved Temporarily (HTTP 1.1 Only)
A 307 redirect is the HTTP 1.1 successor of the 302 redirect. While the major crawlers will treat it like a 302 in some cases, it is best to use a 301 for almost all cases. The exception to this is when content is really moved only temporarily (such as during maintenance) and the server has already been identified by the search engines as 1.1 compatible.
Since it’s essentially impossible to determine whether the search engines have identified a page as compatible, it is generally best to use a 302 redirect for content that has been moved temporarily.
Other redirection types
There are also some other types of redirection: Meta Refresh or JavaScript redirection that are executed on the page level rather than the web server level. This is what a typical Meta Refresh redirect looks like:
It’s best not to use these types of redirect, as they are often used by spammers and doorway pages. Besides, they pass little to none of the link juice.
Examples of using redirects
Redirecting your domain to a non-www URL:
Redirecting your domain to a www URL:
To choose which URL to make canonical, consider:
When developing a website, it’s important to choose whether you want to add a slash to the links, because the search engines consider the links
— www.site.com/cat1
and
— www.site.com/cat1
to be different. Then, you’ll have to add the following code:
To delete the slash from the URLs:
To add the slash to the URLs:
To redirect the user from one page to another:
Redirecting the main page duplicates
This code ensures that if there are multiple versions of the direct link to the main page (index, etc.), they will all redirect to the canonical main page:
If the URLs reflect the structure of a catalog, changes in the catalog will lead to changes in the URLs. In this case, use the following redirect:
But, if the URL of the previous catalog comes right after the name of a domain: www.site.com/old-catalog, use this code:
If you’ve switched platforms or a CMS and only the URLs’ extension has changed, use this redirect:
Examples of using redirection to avoid duplicate pages
In case you’ve bought several domains with multiple TLDs, OR used a subdomain to develop a new website and forgot to block it from being indexed by the search engines. Either way, you have to set up redirection to the root domain:
That way, all the (sub-)domains like www.site.org, www.site.net, test.site.com, will redirect to www.site.com
Deleting multiple slashes/hyphens from the URLs
Sometimes, user can accidentally type in multiple slashes, e.g. www.site.com/catalog////page-1.html. In this case, you have to set up a 301 redirect to a page with a single slash www.site.com/catalog/page-1.html:
In the same way, you can set up a redirect from a URL with multiple hyphens (for example, www.site.com/catalog/page—1.html) to www.site.com/catalog/page-1.html:
Redirecting from any URL to a lowercase URL
The search engines notice the letter case, so it’s best to have your URLs in lowercase. If you haven’t developed your website with this in mind, you can use this PHP-script:
How to move your website to a new domain? The optimal strategy for a 301 redirect
According to the most popular search engines, the best strategy for moving to a new domain is:
Generating 301 redirects
If you’re not particularly tech-savvy, you can use the online services for generating basic redirects:
How to test the 301 redirect
With every change in 301 redirect, you need to test the site’s performance:
301 redirect VS Canonical — which one to use & when?
Minor details aside, in order to understand what exactly do we want to say, Google offers some clear-cut rules. In very simple terms, this is how the search engines understand our commands:
301: okay, google (or any other search engine), my page isn’t there anymore and it’s been permanently moved to a new URL. Please, delete the old link from the index, and pass the link juice to the new page.
Canonical: okay, google, I’ve got multiple versions of the same page (or its content), so, please, index only the canonical version. I will keep the other versions for people to see, but don’t index them, please, and pass the link juice to the canonical page.
When is it better to use a 301 redirect?
When is it better to use rel= «canonical»?
Both solutions pass the link juice and both are ranked by Google equally. 301 redirect is a bit more preferred, though.
Redirection mistakes
If you have any questions, ask them down below. I will try my best to help you!
3 Ways To Redirect A Website URL
When a website is new, the need for redirects may seem foreign. A fresh website with just a few pages is straightforward enough.
But over time, websites grow. As you add more pages and build out more categories, you start to have more URLs to deal with. You may realize late in the game that your URLs are more complex than you’d like.
Or a website audit may lead you to pages that aren’t performing well that should be removed or combined with others. Then what do you do about those old URLs?
Almost all website owners will at some point face the need to set up a redirect.
You might like…
What is a Website Redirect?
A website redirect points your old URL to a new page. When anyone types in or clicks on that original URL they’ll be taken to the page you set the redirect up to instead. It ensures visitors don’t end up on a 404 page and instead find something relevant to what they were originally looking for. And it keeps you from losing the value of any links you’ve built to that page—which is important for search engine optimization (SEO), as well as the user experience of anyone that clicks one of those links.
Knowing how to set up a redirect is a valuable skill for anyone that runs a website. You can implement redirects on a page-by-page basis, or at the domain level.
3 Types of URL Redirects
There are three main types of redirects to be aware of, although most website owners will only need to use the first.
1. 301 Redirect
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect. This type of redirect takes place on both a browser and server level. It’s the most commonly used and powerful redirect. It passes on all the SEO authority of the existing URL. And search engines recognize and index this kind of redirect, making it the best choice for SEO.
In almost all cases, this is the type of redirect you’ll want to use.
2. 302 Redirect
A 302 redirect is a temporary redirect. It should only be used when you have the intention of moving back to the old URL at some point. If, for example, you’re redesigning your site, but want to direct users to a different domain while you finish. Or if you want to A/B test two different versions of a page, before committing to a new version.
302 redirects aren’t used very often. If you’re considering using a 302 redirect, consider carefully whether you might be better off using a 301 redirect.
3. Meta Refresh
Have you ever landed on a page and been greeted with a message that says, “The original URL has moved, you’re now being redirected. Click here if you’re not redirected in 5 seconds”? Then you’ve experienced a meta refresh.
A meta refresh is a redirect that functions by telling the browser to go to the new page, without updating the server. When setting up a meta refresh, you can clarify the amount of time it should take for the redirect to the new page to occur. Sometimes search engines interpret a meta refresh in the same way as a 301 redirect, especially if the time allotted is zero or one second. But it’s not entirely consistent how search engines read a meta refresh, and they create a worse user experience by making the visitor wait to get to the page they’re seeking.
In instances where you’re considering a meta refresh, you’re likely to be better off with a 301 redirect.
How to Set Up a Redirect
Most website owners have multiple ways they can choose to set up a redirect. Here are instructions for three common options.
1. Set up a Redirect in cPanel
When signed into your cPanel account, scroll down to the Domains section. Find the icon for Redirects and click on it.
In the dropdown menu under Type, you can choose between Permanent (301) or Temporary (302). Make your selection.
In the next dropdown menu, choose which domain you’re setting up the redirect for. You can choose All Public Domains if you want the update to apply to all the domains you own, otherwise select the appropriate one from the dropdown.
Then simply fill in the page you want to set up the redirect for, and the page you want it to go to. Note that in the first box, you’ll only put the last part of the URL, since the root domain name is already supplied in the dropdown menu. But in the second box, put in the full URL you want it to redirect it to.
2. Set up a Redirect in Gator
If you use the Gator Website Builder, select Edit Site for the website you want to set the redirect up for.
The select Manage on the menu on the left side of the screen, and Redirects on the menu that opens up from there.
Click the Add Rule button. Enter the page you want to redirect in the box on the left. Select the type of redirect in the dropdown menu.
Then, based on the type of redirect you selected, you can either choose the page you want the old URL to redirect to in the dropdown menu on the right, or you can enter the URL you want it to go to.
Then simply select OK.
3. Set up a Redirect in WordPress
The easiest way to set up a redirect in WordPress is using a plugin. One popular option for this is Redirection.
If you’re new to adding plugins in WordPress, select Plugins in the menu on the left side of the screen. Click Add New, then perform a search for the plugin you want.
Click Install Now, then Activate. Each plugin will have its own instructions for how to use it. For Redirection, find it in your Installed Plugins list, click on Settings, then go through the setup instructions.
Once it’s set up, you’ll be able to find Redirection listed under Tools. Then click on Redirects in the menu at the top of the screen, and fill in the information for the URL you want to redirect, and the new URL you want it to point to.
Then click the Add Redirect button.
5 Reasons Why You’d Create a Website Redirect
Now you’ve got three different ways to set up redirects, but if you’re still wondering why someone would bother with this, there are a few main scenarios where it comes up.
1. Redirect a Subdirectory to a Page on Your Site
When you created your site, you may have decided to create your blog page on a subdomain of your site. So, instead of your blog URL being “mysite.com/blog” you made it “blog.mysite.com”. And now you’ve decided that it makes sense to switch your blog off of the original subdomain structure.
This is a case where you’d set up a redirect. The same goes for any other reason you’ve created a site or section of your site on a subdomain, and now you want to switch the URL structure to something new.
2. Redirect Duplicate Content to the Original Page
Having duplicate content on your site is bad for SEO. If you have a large site, you may well have pages with duplicate content. When you have more than one version of the same page it makes it hard for Google to figure out which page to rank.
Avoid duplicate content issues by redirecting the duplicate piece of content to the original. This will both reduce confusion for your visitors and improve your search engine rankings.
3. Redirect Multiple Domains to a Single Domain
Many brands buy up multiple domain names related to their main URL in order to protect your online brand. If your brand is Acme Corp. you may want to own acme.com, acmecorp.com, acme.net, etc.
Instead of buying domains to keep others from registering them, then just letting them sit there, you can redirect them to your main website. Whether they’re common misspellings of your existing domain name, other top level domain name extensions, or something else entirely, they’re worth redirecting back to your main site.
4. Redirect Your Old Domain to Your New One
Did you originally build out your site on a domain that wasn’t your first choice, then managed to buy your dream domain later on? Or maybe you went through a massive rebrand and changing your domain name is now necessary.
Whatever the reason, you need to implement a redirect of your old domain to your new domain. Now, migrating an entire site is more intensive than a simple redirect, but it’s an important part of the process.
5. Redirect an Old URL to a New URL
Sometimes you have to change the URL of existing pages and posts. Maybe you’re cleaning up your existing URL structure, or you moved some pages around and the old URL no longer makes sense.
In this case, you’ll want to implement a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new one. This is especially true if your older posts are already indexed in the search engines, or have links pointing to them anywhere online.
Conclusion
Setting up a redirect may seem intimidating at first for the non-technical website owners out there. But with several intuitive options, it’s a task you should be able to tackle on your own. And using redirects well can help you update your website over time to be more useful, avoid 404 errors, and improve SEO.
Kristen Hicks is an Austin-based freelance content writer and lifelong learner with an ongoing curiosity to learn new things. She uses that curiosity, combined with her experience as a freelance business owner, to write about subjects valuable to small business owners on the HostGator blog. You can find her on Twitter at @atxcopywriter.
Every developer has a
tab open to
Stack Overflow
A public platform building the definitive collection of coding questions & answers
A community-based space to find and contribute answers to technical challenges, and one of the most popular websites in the world.
A private collaboration & knowledge sharing SaaS platform for companies
A web-based platform to increase productivity, decrease cycle times, accelerate time to market, and protect institutional knowledge.
Thousands of organizations around the globe use Stack Overflow for Teams
Capture your company’s knowledge and context in a discoverable format to unblock your team
Increase productivity
If somebody somewhere has the right answer, suddenly you have it too. Collaborate better in a remote-first world.
Accelerate time to market
Shorten the time between initial idea and complete product. Take delays and misinformation out of the equation.
Protect institutional knowledge
People come and people go, but if you capture their contributions in one central place, that expertise sticks around.
Ensure your company stays on course
Here are just a few types of technologists that we help.
DevOps engineers
Shipping new products and features requires teamwork and coordination. Forget checklists and long docs no one ever reads.
Data scientists
Business decisions are better when backed by data. Give visibility to the data that support your strategies.
Software engineers
Help engineers be more efficient and streamline knowledge sharing using a tool they already love and trust.
Support teams
Level up your support by providing information to your customers using a natural interface: questions and answers.
Engineering leaders
Free knowledge sharing and collaboration platform
Always free up to 50 teammates
Basic
Centralized knowledge and collaboration platform for small and growing teams
Up to 250 teammates
Business
For small and medium sized businesses seeking advanced administrative tools
Enterprise
For medium to large businesses with additional security, configurability and content management needs
Integrates with and improves other tools
All plans come with integrations for ChatOps tools Slack & Microsoft Teams in order to cut down on pings, limit distractions and make the tools even more powerful. Business and Enterprise customers get access to Jira, GitHub & Okta integrations.
Robust read and write API
Single sign-on with AD or SAML
Your own customer success representative
99.5% uptime SLA and priority support
Stack Overflow for Teams has been a resource for our entire company. Not only for developers to solve problems, it’s also enabled our sales field to answer technical questions that help them close deals.
Engineers should help solve the hardest questions, the unknowns, where being familiar with how the product was built is essential. But we don’t want to keep answering solved problems over and over again. That’s where Stack Overflow for Teams really helps.
As we started to use [Stack Overflow for Teams] and saw how nice it was to have a repository of information, we started to see it spread to other teams. Our customer support team started using it, our people success team started using it, next thing we knew, we had [Slack] integrations all over the place.
What we love about Stack Overflow for Teams is that it’s a very dynamic tool…there’s just so many ways to use this as a liaison between different teams and different knowledge bases.
Additional products that reach and engage developers & technologists…
Reach the world’s largest audience of developers and technologists
Connecting communities with the specific technologies they use the most
Build your employer brand to attract tech talent
Programming & related technical career opportunities
Explore technical topics and other disciplines across 170+ Q&A communities
From Server Fault to Super User, much of the Stack Exchange network continues our mission to empower the world to develop technology through collective knowledge. Other sites on the Stack Exchange network further encourage knowledge sharing across topics such as cooking and medicine.
Build a private community to share technical or non-technical knowledge.
site design / logo © 2021 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under cc by-sa. rev 2021.9.17.40238
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
How to Easily Make HTML Redirect to Another Page
Web Development Course:
TL;DR – HTML redirect takes a website visitor to another site automatically.
Contents
What is an HTML Redirect?
A redirect happens when a user enters a URL, but it changes, and the browser takes them to a different one instead. Website creators rely on them when they need to change the structure of their site or the location of a particular page. Of course, you may redirect to a completely different website as well.
When working with Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), you need to have a basic understanding of its response codes. They contain three digits, first of which defines their type: